Contents:
In the numismatic world, certain coins like the 1974 quarter may be rather valuable, and knowing what to look for can turn a casual collector into a respected numismatist.
Why is the 1974 quarter value worth exploring? Because amidst the millions of quarters minted that year, there are rare ones with errors and unique details that make certain coins much more expensive than others.
Today, you will understand how much is a 1974 quarter worth and will know how to identify coins that could potentially change your financial future.

Numismatic Description of the 1974 Quarter
Feature | Details |
Year | 1974 |
Designer | John Flanagan |
Composition | 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel |
Diameter | 24.3 mm |
Weight | 5.67 grams |
Mint Marks | No Mint Mark (Philadelphia), "D" (Denver), "S" (San Francisco - Proofs) |
Edge | Reeded |
Historical Background and Design
The 1974 quarter belongs to the long-standing Washington quarter series, which first entered circulation in 1932. This series was created to honor the bicentennial of George Washington's birth (200 years since the first president's birth).
Planning for this monumental celebration began well before the event, with Congress passing legislation in 1930 to establish a Bicentennial Commission. Among their key initiatives was launching a design competition for a new coin featuring Washington’s portrait. The design was to be based on a bust created by renowned French sculptor Jean-Antoine Houdon.
Laura Gardin Fraser, an accomplished artist, won the competition with her design. The Commission requested her to adapt it for a commemorative medal and a proposed Washington half dollar, intended to replace the existing Walking Liberty half dollar.
However, Congress ultimately chose to redesign the Standing Liberty quarter instead. Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon bypassed Fraser’s design in favor of one by sculptor John Flanagan, leading to tensions between the Bicentennial Commission and the Treasury Department. Despite the disagreements, Flanagan’s work was selected for the Washington quarter.
By mid-1932, a few years before the 1940 nickels were minted, the new quarter was being struck, and it entered circulation in August of that year. Over the years, the design of the Washington quarter saw minor adjustments but remained largely consistent.

Transition from Silver to Copper-Nickel Composition
The mid-20th century brought changes to U.S. coinage. A shortage of coins in the early 1960s because of rising silver prices led to widespread hoarding. In response, the Mint increased production, but the problem persisted as both silver and base-metal coins were stockpiled.
To address this, Congress passed the Coinage Act of 1965, which eliminated silver from circulating coins, including the Washington quarter. Starting that year, quarters were made from a copper core with an outer layer of copper-nickel. This composition remained the standard for the 1974 quarter.
Design Features
The design of the 1974 quarter stayed true to the original Washington quarter concept, with minor updates. Here is a closer look at the obverse and reverse of the coin:
Obverse (Front):
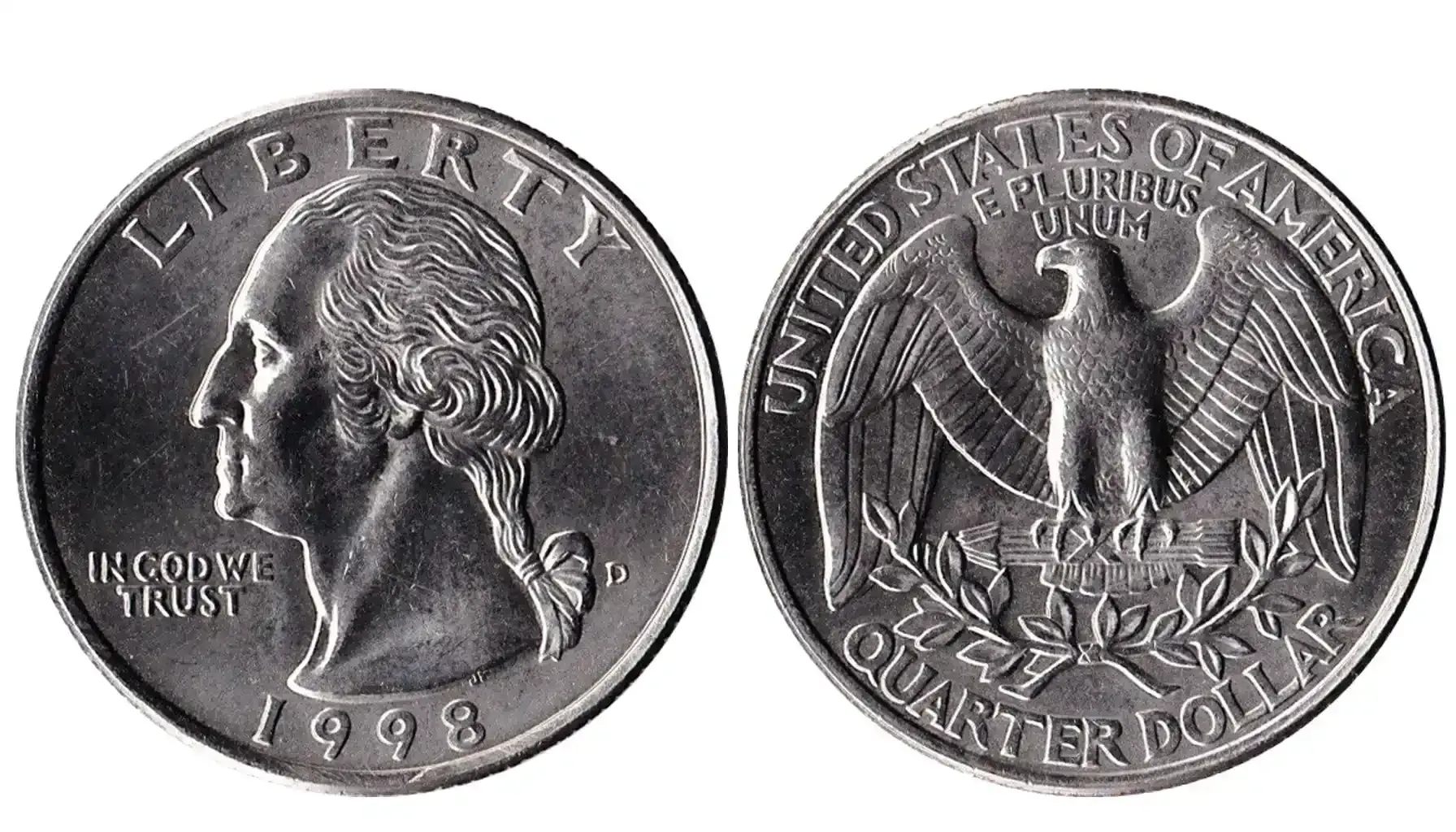
The obverse displays a left-facing portrait of George Washington, modeled after Houdon’s 1785 sculpture. The word LIBERTY is prominently placed along the upper rim.
The national motto, IN GOD WE TRUST, appears to the left of Washington’s neck. The date, 1974, is inscribed at the bottom rim.
The initials "JF," representing designer John Flanagan, are etched subtly above the "4" in the date near Washington’s collarbone.
Reverse (Back):
The reverse features an American bald eagle with outstretched wings, perched on a bundle of arrows—a symbol of strength and readiness to defend the nation. The image is framed by two olive branches, representing peace.
The top of the coin bears the inscription UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, while the phrase E PLURIBUS UNUM is positioned just below it, as if resting on the eagle’s head.
The denomination, QUARTER DOLLAR, is inscribed along the lower rim.

What Is the 1974 Quarter Value?
It depends on several factors, e.g., condition, mint mark, and whether it contains any errors. For most circulated quarters, the value is modest. However, rare errors or high-grade examples can increase the coin’s worth.
1974 Quarter No Mint Mark: Minted in Philadelphia, these coins lack a mint mark. While most are worth face value, uncirculated or error examples can fetch $20 or more.
1974 D Quarter: Produced in Denver, these coins are also common, but pristine conditions or errors can elevate their value to $25 or more.
1974 S Proof Quarter: Proof coins from San Francisco are highly sought after for their craftsmanship. These typically range from $3 to $10.
1974 Quarter Errors That Are Worth Money
Minting mistakes can transform an ordinary quarter into a valuable collectible. Here are some of the most notable errors found on 1974 quarters:
Off-Center Strikes: Coins struck off-center are highly collectible. Values range from $50 to $500. Total price depends on the degree of misalignment.
Double Die Errors: Doubling on the inscriptions or date is rare but valuable. These coins can cost hundreds of dollars.
Clipped Planchet: A portion of the coin is missing due to a minting error. These are worth $100 to $400.
Wrong Planchet Errors: Occasionally, a quarter is struck on a dime planchet, creating a unique collectible. This ties into the 1974 dime error list and can fetch high prices.
Wrong Metal Composition: Rare cases of quarters struck on leftover silver planchets instead of copper-nickel are worth thousands. The 1974 silver quarter value can go up to $1,000 or more in such cases.
One of the most exciting finds in this category is the error 1974 quarter worth 35000 $. Coins like these are highly coveted due to their rarity and the dramatic nature of the error.

How Much Is a 1974 Quarter Worth With No Mint Mark?
If you have found a 1974 quarter with no mint mark, it was minted in Philadelphia. While most are common and worth face value, pristine uncirculated examples or error coins can be far more valuable. For most, the value is between $0.25 and $1, but collectors pay more for rare features or high grades.
Type | Condition | Estimated Value |
1974 Quarter Value No Mint mark | Circulated | $0.25 - $1 |
Uncirculated (MS65) | $5 - $25 | |
1974 D Quarter Value | Circulated | $0.25 - $1 |
Uncirculated (MS65) | $5 - $30 | |
1974 S Quarter Value | Proof Condition | $3 - $10 |
1974 Quarter Error Value | Varies (Details Below) | $50 - $35,000+ |
Disclaimer: Values fluctuate based on condition, market trends, and demand. Consult professional appraisers or grading services for accurate assessments.
Grading Coins
Grading coins is one of the most crucial steps in determining whether your 1974 quarters worth money. The grade of a coin directly impacts its desirability among collectors and investors.
Coin grading is the process of assessing a coin's physical condition and assigning it a grade on a standardized scale. The most widely used system is the Sheldon Scale, which ranges from 1 to 70, with 70 representing a perfect, flawless coin.
Poor (P-1): The coin is barely identifiable, often heavily worn and damaged.
Good (G-4 to G-6): Basic details are visible, but the coin shows heavy wear.
Fine (F-12 to F-15): Moderate wear with major design elements still discernible.
Very Fine (VF-20 to VF-35): Light wear on high points, with strong details elsewhere.
Extremely Fine (EF-40 to EF-45): Slight wear on the highest points, with sharp overall detail.
About Uncirculated (AU-50 to AU-58): Nearly no wear, with minor scuffing on the highest points.
Mint State (MS-60 to MS-70): No wear at all; coins graded MS-65 or higher are exceptionally well-preserved and highly valued.
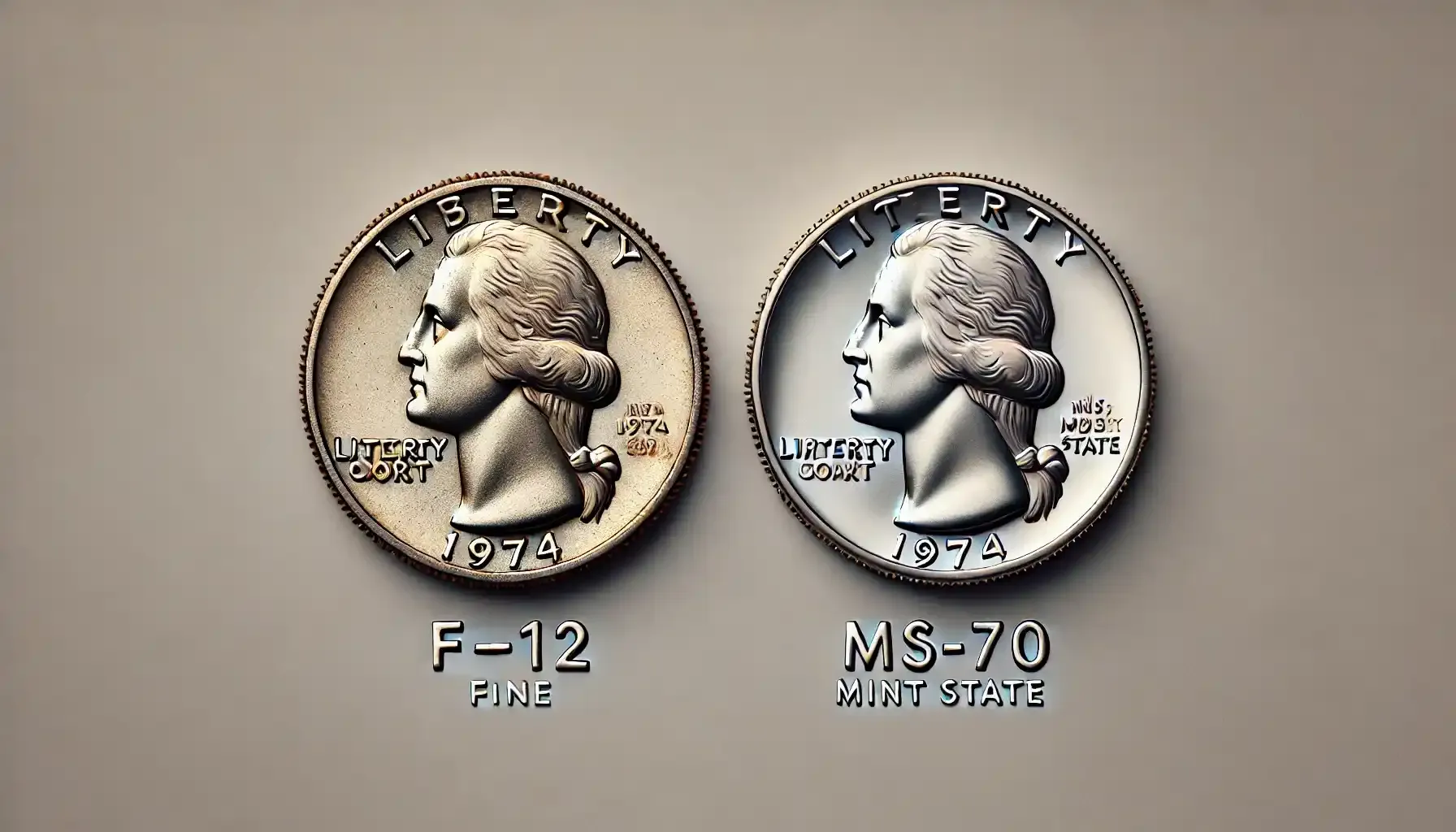
Why Grading Matters for the 1974 Quarter
Coins like the 1974 quarter benefit greatly from accurate grading, as the value can increase exponentially for coins in higher grades. For example:
A circulated 1974 quarter might only be worth its face value.
An uncirculated 1974 quarter graded MS-65 could be worth $20 or more.
A value rare 1974 penny error graded MS-67 or MS-68 can sell for thousands, especially if it is well-preserved.
How to Grade Coins Yourself
While professional grading is ideal, you can do a preliminary assessment of your 1974 quarter at home. Here is how:
Clean Environment: Work in a well-lit area and use gloves or hold the coin by its edges to avoid fingerprints.
Magnification: Use a loupe or magnifying glass to examine small details, including date, mint mark, and surface imperfections.
Reference Guides: Compare your coin to high-resolution images in coin catalogs or online databases to identify its approximate grade.
Document Condition: Note any wear, scratches, or irregularities that might impact the grade.

Professional Grading Services
To get an official grade for your coin, consider sending it to a professional grading service. The most trusted organizations include:
Professional Coin Grading Service (PCGS): Known for their stringent grading standards and secure encapsulation of graded coins.
Numismatic Guaranty Corporation (NGC): A leading grader offering detailed assessments and tamper-proof holders.
American Numismatic Association Certification Service (ANACS): A reputable option, especially for older or unique coins.
Apps and digital tools have made it easier to get preliminary assessments. The Coin ID Scanner app, for example, allows users to photograph their coins, even modern ones like the 2005 Buffalo nickel, and receive instant feedback on potential grades and values. While these apps cannot replace professional services, they are excellent for quick evaluations.
For a 1974 coin, errors such as double die strikes, clipped planchets, or wrong planchet compositions can affect grading. Even lower-grade coins with rare errors may command high prices. Ensure any error is certified by a grading service to maximize its value.



