Contents:
Did you know that some coins can hide something more valuable than its stated worth in daily circulation? One may believe that the 1984 quarter is just another numismatic creation with ordinary features and history to forget. Nevertheless, its rare varieties and errors have turned this presumably common piece into a collectible.
In this material, we are to discover the 1984 quarter value and the diversity of the quarter types. Learn more about how to identify coins with rare errors and why it might be the right time to take a closer look at the coins in your pocket.

What About the Washington Quarter series?
In American coin history, the Washington Quarter series remains one of the most recognizable and iconic coin designs ever minted. Back then, in 1932 (the 200th anniversary of George Washington's birth), it was meant to be a one-year commemorative coin. However, because of its popularity, it was turned into a continuous circulating series, used for decades as the standard design for the quarter-dollar denomination.
As time passed, so did the design of a coin:
1932–1964: The quarters consisted of 90% silver and 10% copper, which made a valuable asset thanks to their metal content.
1965 and onward: The composition gradually changed to a copper-nickel clad, with two layers of nickel encasing a core of pure copper, as a result of the increased price of silver starting in 1965.
Just like the majority of modern coins, these were produced by the main Mints located in Philadelphia (with no mint mark), Denver (with a "D" mint mark), and San Francisco (with an "S" mint mark for proof pieces). Although ordinary issues may not be exceptional, their deviations are particularly collectible because of their exclusivity and elaborate designs.
The Appearance and Features of the 1984 Washington Quarters
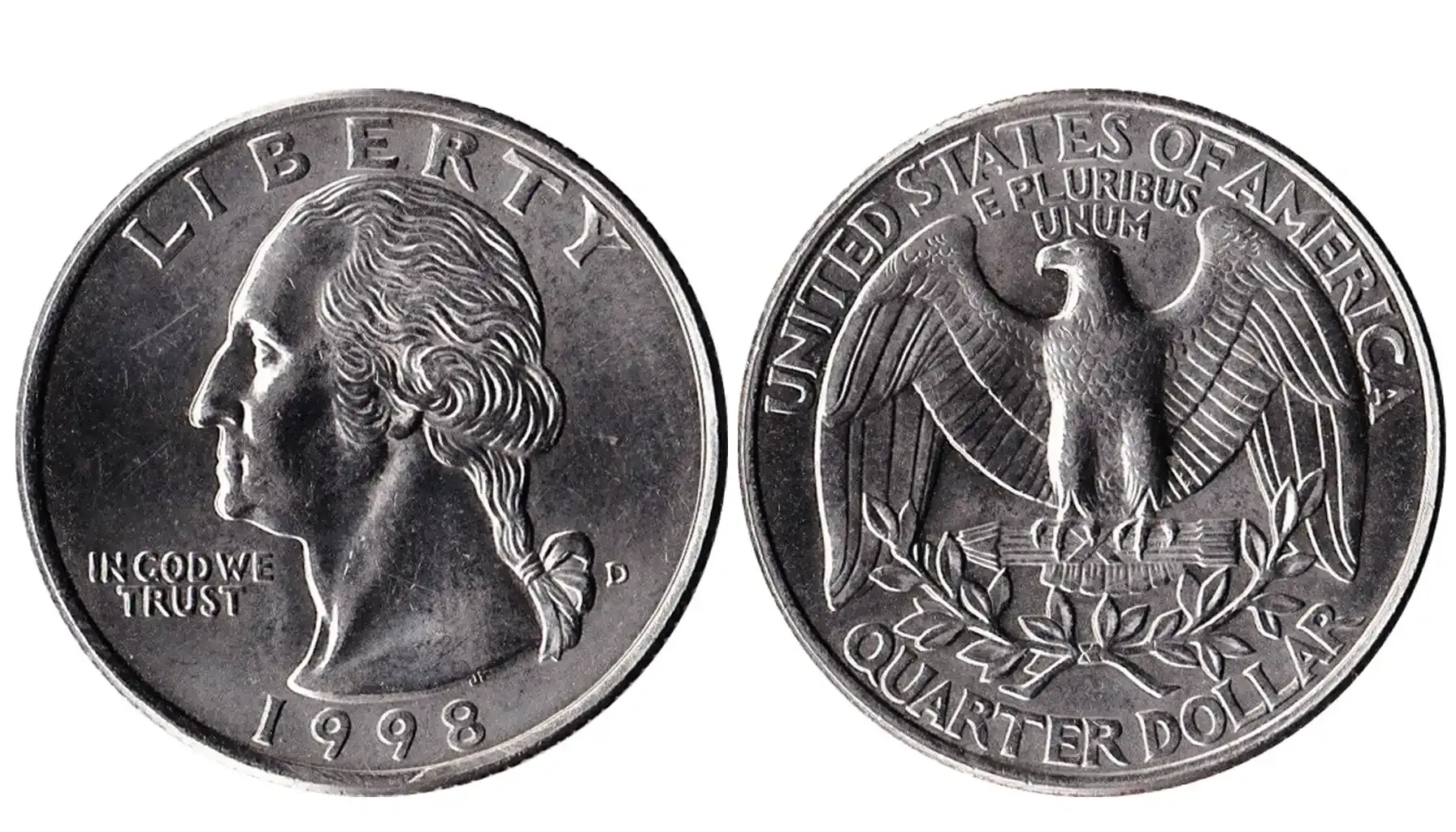
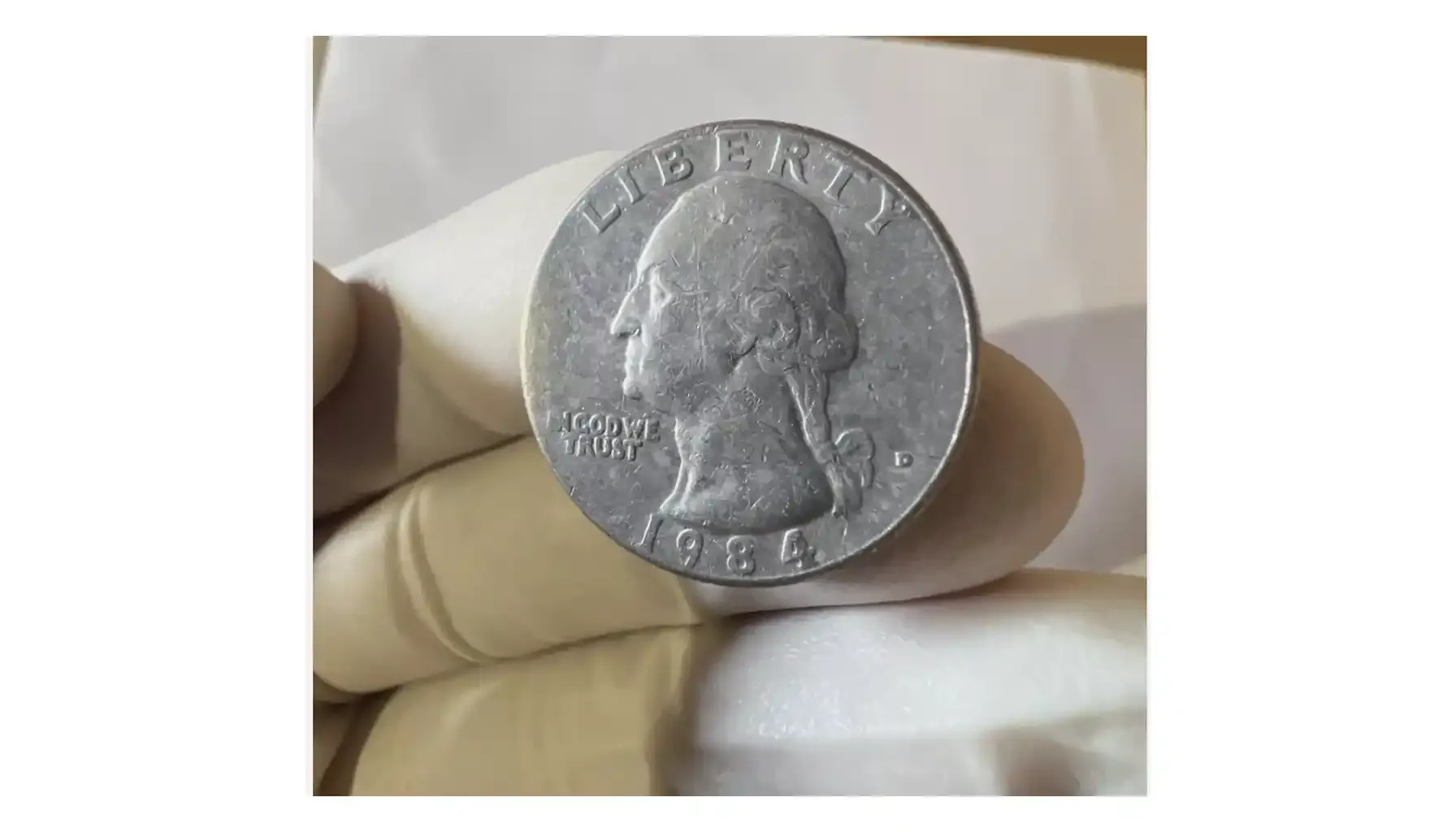
It is true that numismatists and the general public (especially those native to the US) appreciate the quarter 1984 value and the classic design of the coin. Take a look at the table below to explore the main characteristics of this creation.
Obverse Design | A left-facing profile of George Washington, the first president of the United States, surrounded by the inscriptions “LIBERTY” (above Washington’s head), “1984” (below the bust), and “IN GOD WE TRUST” (to the left of Washington’s profile). |
Reverse Design | An image of a bald eagle perched on a bundle of arrows with two olive branches below and the inscriptions “UNITED STATES OF AMERICA” and “E PLURIBUS UNUM” at the top. |
Composition | Outer layers of 75% copper and 25% nickel, with a core of pure copper. |
Weight | 5.67 grams |
Diameter | 24.30 millimeters |
Edge | Reeded |
As usual, there are three main US Mint sites responsible for the production of coins. The 1984 quarters were no exception. The largest manufacturing facility is the Philadelphia Mint, which released instances with no mint marks at all. Denver, in turn, minted coins with "D" marks on the obverse, immediately beneath the phrase "IN GOD WE TRUST". Lastly, the San Francisco Mint was responsible for the production of proof coins ("S") with sharper details and a mirror-like polish.
Philadelphia Mint: 676,545,000 pieces
Denver Mint: 546,483,064 pieces
San Francisco Mint: 3,065,110 pieces
1984 Quarter Errors and Varieties
Any deviation makes a difference. These are exclusive, quite notable, and one-of-a-kind. Below, we have prepared a quick yet rare 1984 quarter error list for one to keep track of:
Doubled die errors (design elements appear doubled)
Off-center strikes (misaligned strikes that leave part of the design missing)
Clipped planchets (circular or crescent-shaped clips on the edge)
Die cracks and cuds (raised lines or blobs from damaged dies)
Broadstrikes (coins struck without a retaining collar)
Struck-through errors (impressions from foreign material interfering during minting)
Repunched mint marks (RPM) (overlapping or doubled mint marks)
How Much is a 1984 Quarter Worth?
Is a 1984 quarter worth anything? Yes, for sure, yet the final estimation can only be made on the basis of its type, condition, and presence of errors or other distinctive features. Even though there are still a lot of 1984 quarters in circulation, numismatists are able to locate exceptional units and incorporate them into their collections.

Circulated Quarters
The majority of 1984 quarters that are used in regular transactions are worth their face value of 25 cents. This can be one of the first coins to be obtained since these are generally accessible and more common.
Uncirculated Examples
Uncirculated units, in turn, are more valuable, for they are still undamaged and may boast their original luster. These can be sold for anywhere from $1 to $5, which mainly depends on the grade. Higher-grade instances can get even higher values, particularly those that have been given an MS65 or higher grade by professional services, e.g., PCGS or NGC.
Proof Coins
As we have mentioned above, In 1984, the San Francisco Mint issued proof quarters aimed specifically at collectors. Higher-graded or exceptionally pristine examples may fetch higher prices, with their usual value falling between $3 and $10.
Error Coins
The 1984 error quarter with major anomalies, like clipped planchets, off-center strikes, or duplicated dies, can be quite valuable, and auction sites demonstrate this phenomenon at its best. To be more precise, they may easily sell for $20 to several hundred dollars, depending on the origin and rarity of the error. This is particularly relevant if the coins are visually striking or have been certified by grading services.

How to Identify and Authenticate Rare 1984 Quarters
Check Mint Errors
Verifying mint faults is one of the most crucial steps in recognizing unusual 1984 quarters. The most frequent occurrence refers to double die errors, in which a portion of the design is imprinted more than once. The more elaborate and distinctive this error is, the more valuable the coin can get. Pay attention to the coin's inscriptions and date, particularly if they seem blurry or misaligned. Although these are harder to find, these coins can be priced higher.
Verify Uncirculated State
A 1984 quarter can also be identified by its condition. Coins that have never been used or that have been stored in perfect condition are always worth more than ones that are worn out or broken. A coin of the grade "Mint State" or "Proof" has a great chance of being collected, especially when it is intact or free of blemishes.
Use Tools for Pre-Evaluation
Before you spend money on expert grading services, it might be reasonable to assess the authenticity and rarity of your 1984 quarters with the use of a modern tool, such as Coin ID Scanner. In order to find out whether a coin is precious or rare, these programs can scan its properties via the camera on your smartphone and compare them to databases of known cases.
Besides, one may get real-time updates regarding coin prices and keep track of the collectibles that have already been obtained.
Authenticate with Professional Grading Services
So as to authenticate a rare 1984 quarter, or any other like Aztec coins, and assess its condition, serious collectors may need to appeal to professional grading organizations like the Professional Coin Grading Service (PCGS) and the Numismatic Guaranty Corporation (NGC).
Look for Special Editions
In addition to errors and mint conditions, some instances might be part of special sets or series that were produced in limited quantities. Proof coins, for example, can be included in any collection and make it worth more than its face value if you find one.
How much is a 1984 quarter worth today? More than you could imagine. These coins remind us that even everyday change should be studied and discovered. Check your change, revisit your coin stash, and examine every quarter with curiosity.



